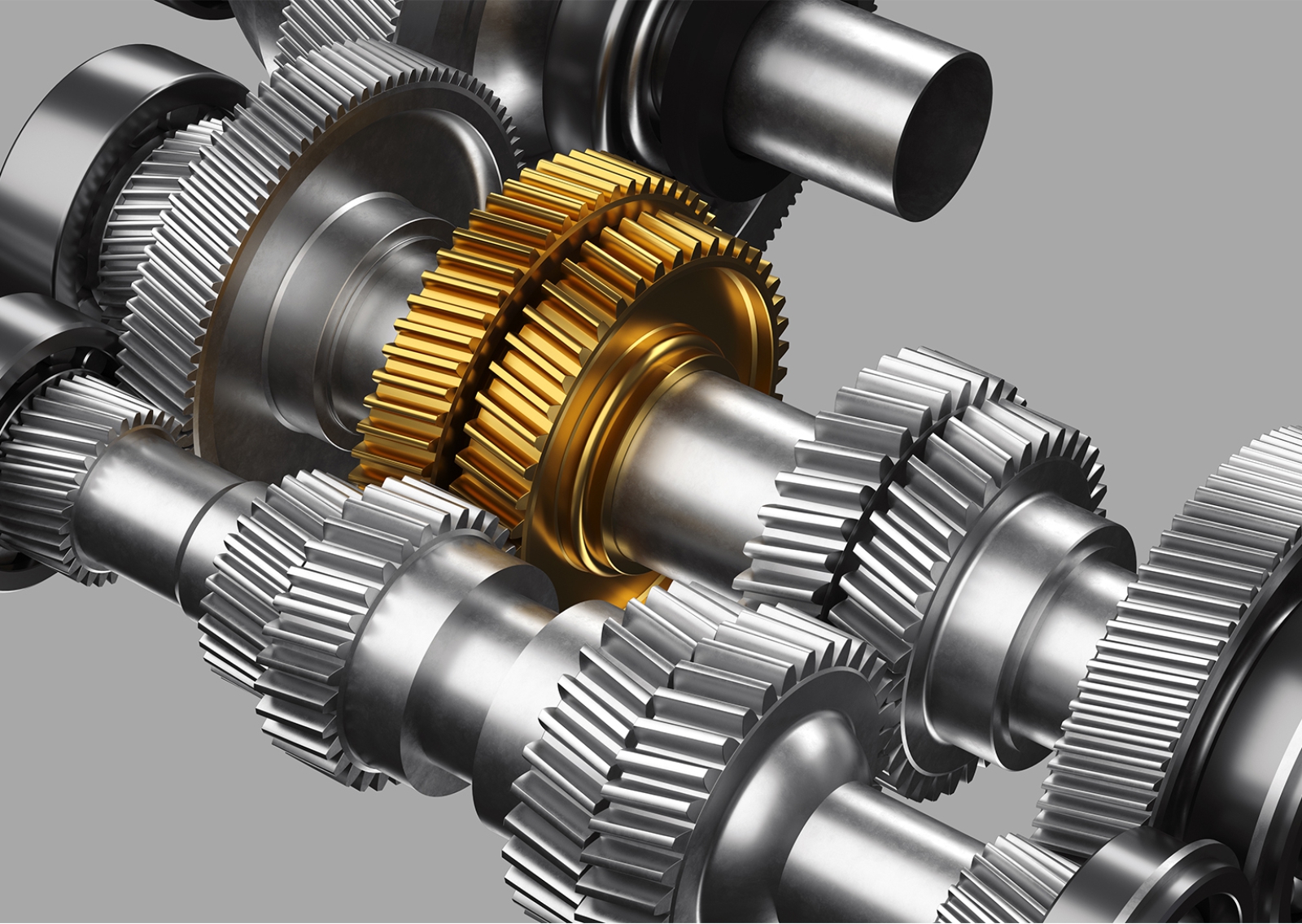
Transmission Gear Definition
Transmission gear is the gear system that transmits the power and torque produced by the engine to the wheels in accordance with the speed and road conditions of the vehicle. Different types of transmissions such as manual, automatic, CVT and dual clutch (DCT) have different gear systems.
Task and Working Principle of Transmission Gears
✔ Transmitting the Power Produced by the Engine to the Wheels - Provides speed and torque balance.
✔ Providing Different Gear Ratios - Helps the engine run efficiently.
✔ Improving Vehicle Performance and Fuel Efficiency - Provides the best efficiency with appropriate gear ratios.
Providing Reverse Gear and Neutral Position - It can change the direction of movement of the vehicle or make it neutral.
Transmission Gear Types
- Spur Gears → Low cost, noisy but efficient.
- Helical Gears → Quiet, durable and highly efficient.
- Synchromesh Gears → A type of gear that facilitates gear shifts.
- Planetary Gears → Used in automatic transmissions, compact and efficient.
Areas of Use of Transmission Gears
- Automobiles and Trucks (Manual and automatic gearboxes)
- Motorcycles (Smaller and lighter gear systems)
- Agricultural Machinery and Construction Machinery (Transmission systems carrying heavy loads)
- Railway and Aviation Systems (Systems requiring special high torque and speed)
